Public Key Encryption
How Public Key Encryption Works
Public Key Encryption (PKE) allows for both secrecy and authentication to occur
with data. Unlike symmetric (private key) encryption methods, which require a
single key to be used to both encrypt and decrypt the data, Public Key
Encryption uses two keys, one of which is made public and the other is kept
private. The first method where a single key is used requires that the key be
transmitted from the sender to the receiver so they can decrypt the message and
thus there is a chance that the key be intercepted and so the data decrypted by
someone who is not allowed to see it. With PKE the private key is kept secret
and is never transmitted, thus it cannot be intercepted.
The two keys consist of large prime numbers, the larger the better as this will
make them harder to guess and harder to “brute force” or break by trying every
possible combination.
We will therefore discuss how the two keys work together to allow for encryption
and authentication to work.
Encryption
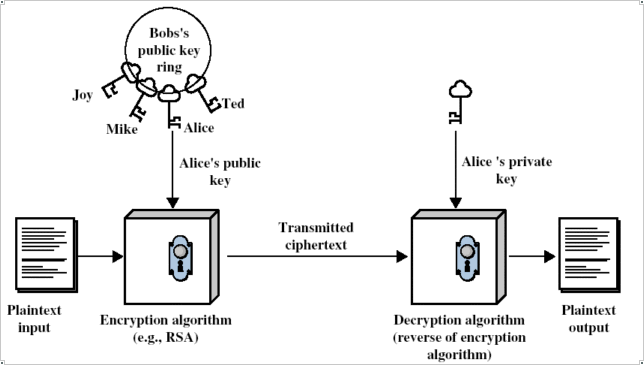
Our explanation of PKE includes two keys and three people.
We call them Alice, Bob and Eve. Bob wants to send Alice a message,
but it contains sensitive information and he doesn’t want Eve to be able
to read it. Bob retrieves Alice’s public key and, using an algorithm, such as
RSA, encodes the message. Bob then transmits it to Alice. Alice receives the
message and, using her private key that only she has access to, decodes the
message back into clear text and is able to read Bob’s sensitive information.
Unfortunately, Eve intercepted the message and wants to know what it says. Eve,
thinking she is quite clever gets hold of Alice’s public key and tries to decode
the message. Since the algorithm used to encode the message is a one way algorithm,
only the second key can decrypt the message and so when Eve attempts to decrypt the
message, all she gets is garbage.
Authentication
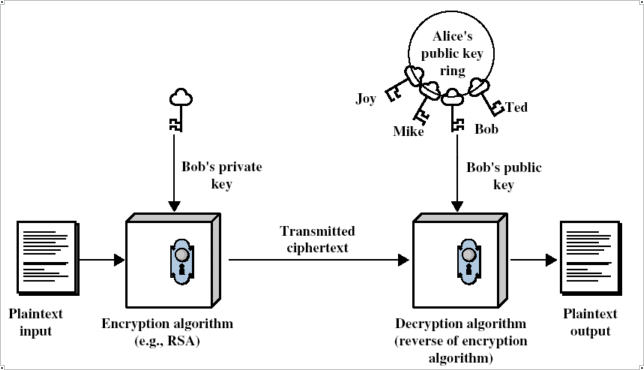
Authentication works like Encryption does but in the opposite way. This time the
sender encodes the message with their private key and anyone wanting to view
the message can decode it with the sender’s public key. We will use the same
actors as above to demonstrate this.
So, Bob now wants to send Alice a message but it contains some important
information about a critical decision he has made. Bob uses his private key and
encodes the message using the encryption algorithm. He then sends this to Alice
as coded text. Alice receives the message and retrieves Bob’s public key and
uses this to decode the message. Looking at the message she sees that
everything looks ok and can now assume that since only Bob has the other key,
the private key, only he could have sent it and hence she has authenticated the
message is from him. If Eve tried to send a message to Alice claiming to be Bob
then since she does not have Bob’s private key she cannot encode the message
correctly. If Alice received a message from Eve claiming to be Bob then after
attempting to decode the message from Eve, Alice would find that the message is
not proper text and so can safely assume that the message is not authentic and
not from Bob.
With authentication though the message is readable by anyone as the only key
that can decrypt the message is made public and so people intercepting the
message can read it.
Combining Encryption and Authentication
3The
methods of Encryption and Authentication can be combined to allow for a message
to be sent from a single source to someone else and it can be guaranteed to be
from that source and also be unreadable to anyone except the appropriate
receiver.
The sender must first use their private key to encode the message and then
encode this coded text again using the receiver’s public key. When the receiver
gets the message, they use their private key to unravel the first layer of
encoding. They then obtain the senders public key and decode the next layer of
text to reveal the decoded text and if it is readable then they can be sure
that it did indeed come from the sender they thought. Since one of the keys is
kept private for encrypting and one is kept private for decryption then it can
be guaranteed that the message is encrypted and only one specific sender could
have sent it and only one specific person could receive it and understand it.
|